3d Ultrasound Down Syndrome
3d ultrasound down syndrome. Ultrasound cannot diagnose a fetus with Down syndrome trisomy 21. Ultrasound cannot diagnose a fetus with Down syndrome trisomy 21. An ultrasound can detect fluid at the back of a fetuss neck which sometimes indicates Down syndrome.
One or more abnormalities were found in 31 fetuses 33 including two of 11 fetuses seen before 14 weeks 17 of 68 fetuses seen between 14-24 weeks and 12 of 15 fetuses seen after 24 weeks. Cell-free DNA has a detection rate for Down Syndrome of 99. 3D ultrasound is a major advance in the noninvasive office-based diagnosis of CUAs.
If the 2D ultrasound does not demonstrate two nasal bones then 3D ultasound may be useful. Approximately 30 of babies with Down syndrome have detectable abnormalities on the mid-trimester ultrasound 1. The technique enables visualization of the uterus in the coronal plane depicting both.
All babies at this stage in pregnancy have some fluid in this area but a baby with Down syndrome or another chromosome abnormality tends to have more fluid. It can pick up soft markers for downs. It can pick up soft markers for downs.
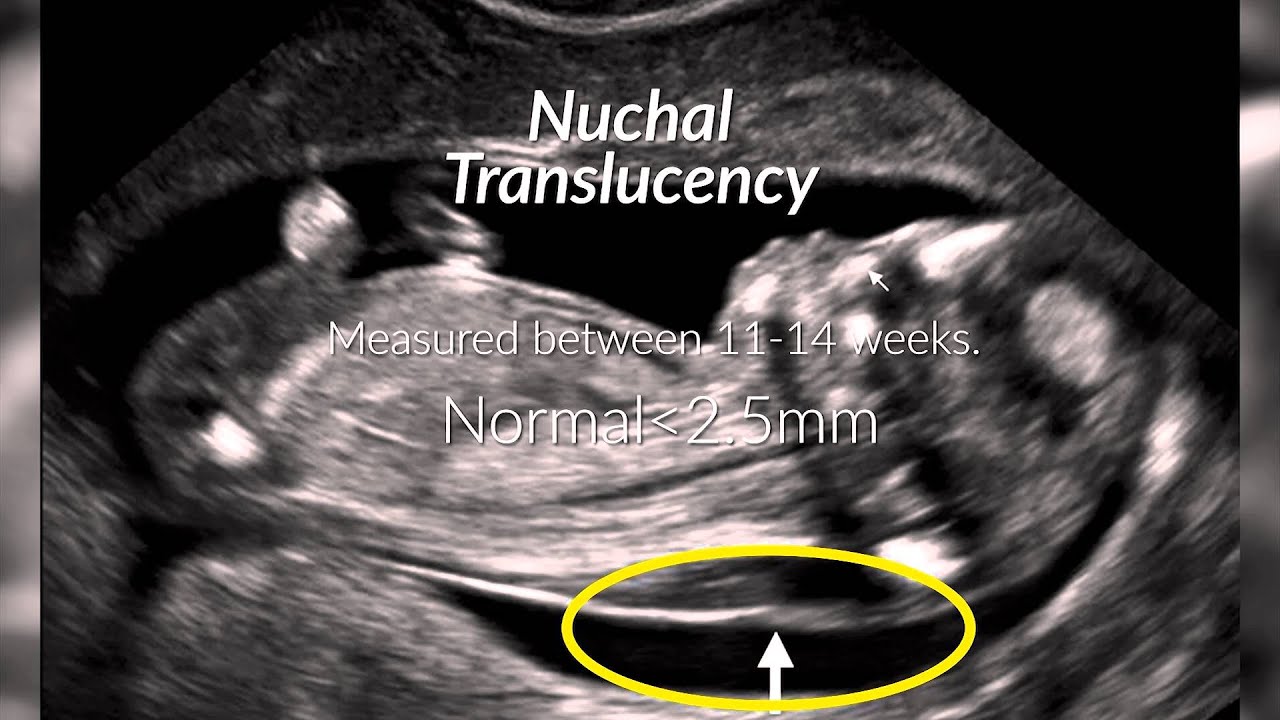
B 2D ultrasound of the fetal profile in which the measured lower face angle is 4706 normal defined as 492. Down syndrome is a genetic abnormality involving an extra 21st chromosome. This is done to measure the thickness of fluid behind the babys neck called nuchal translucency.
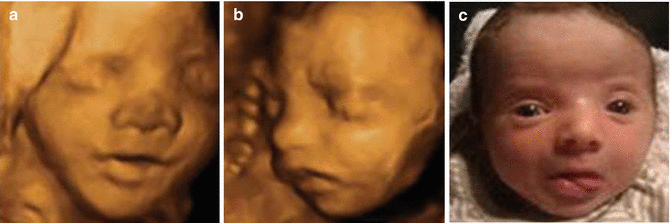
Usually taken between 12- and 13-weeks during pregnancy. The images and video show 3D visualization of mildly stigmatized fetus with Down syndrome. If you indeed identify soft markers a di.
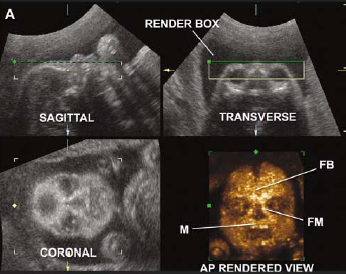
The case is an example where 3D imaging made a disservice regarding searching for facial dysmorphology because the face actually looked normal and cute although 2D imaging see 2D images below - images 6 7 showed hypoplastic nasal bone. C 3D ultrasound surface rendering of the axial plane with the flipped face technique.
If you indeed identify soft markers a di.
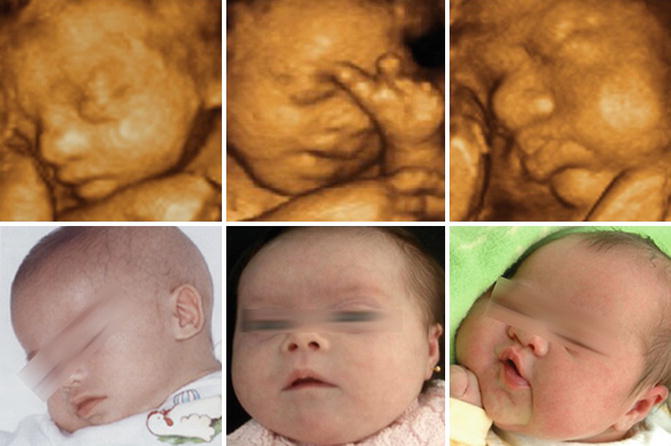
This is done to measure the thickness of fluid behind the babys neck called nuchal translucency. The case is an example where 3D imaging made a disservice regarding searching for facial dysmorphology because the face actually looked normal and cute although 2D imaging see 2D images below - images 6 7 showed hypoplastic nasal bone. The following are ultrasound markers that are seen more frequently in fetuses with Down syndrome. Ultrasonography is the imaging modality mainstay of prenatal screening and diagnosis of Down syndrome and it is often used in combination with biochemical tests. Approximately 30 of babies with Down syndrome have detectable abnormalities on the mid-trimester ultrasound 1. For example a fetus with Down syndrome can have one nasal bone that appears normal and the second bone hypoplastic or absent. During the first trimester this combined method results in more effective or comparable detection rates than methods used during the second trimester. Images 1 2 3 4 5 and video 1. Soft markers are sonographic findings that do not in themselves cause any adverse outcomes.
This measurement is called a nuchal translucency. C 3D ultrasound surface rendering of the axial plane with the flipped face technique. This is done to measure the thickness of fluid behind the babys neck called nuchal translucency. This is an effective way of down syndrome detection. If you indeed identify soft markers a di. B 2D ultrasound of the fetal profile in which the measured lower face angle is 4706 normal defined as 492. It can pick up soft markers for downs.











/GettyImages-157144755-56a773123df78cf772960e9a.jpg)








/babyboyultrasound-7bf2ced4b4794754b67dea974b7ec744.jpg)













Post a Comment for "3d Ultrasound Down Syndrome"