Parkinson's Disease And Dysphagia
Parkinson's disease and dysphagia. Although most of these patients recover their swallowing function in a short period dysphagia in Parkinsons disease PD and Parkinson-related disorder PRD degenerates with disease progression. Oropharyngeal and esophageal dysphagia are a frequent but seldom diagnosed symptom of Parkinsons disease PD. Recurrent pneumonias Diminished voluntary cough effort 1.
Especially in early stages the causal association between d. Dysphagia can be due to the muscular rigidity often present in the Parkinsons diseases patient or more usually by non Parkinsons disease associated causes. OTHER POTENTIAL RISK FACTORS OR SIGNS.
In Parkinsons diseases patients sialorrhea is produced by saliva retention. Problems with tongue muscles. This guideline provides recommendations for speech-language pathology management of Parkinsons disease.
Parkinsons Oral motor disorders are common Dysarthria occurs in about 90 of individuals Drooling occurs in about 78 of individuals Depending on how sensitively dysphagia is measured and treatments are introduced swallowing problems occur in nearly 100 of PwP at. Swallowing Dysfunctions in Parkinsons Disease. Parkinsons and dysphagia Dysphagia can develop at any point during Parkinsons disease with reported frequency ranging from 30 to 82.
Less efficient muscles may also reduce the tightness that you have when closing your lips making it hard to swallow. Dysphagia is very common in PD affecting over 80 of individuals reflecting the underlying motor impairments and the extent of the diseases progression. If swallow dysfunction is suspected a swallow evaluation can pinpoint what the problem is and swallow therapy can help improve it.
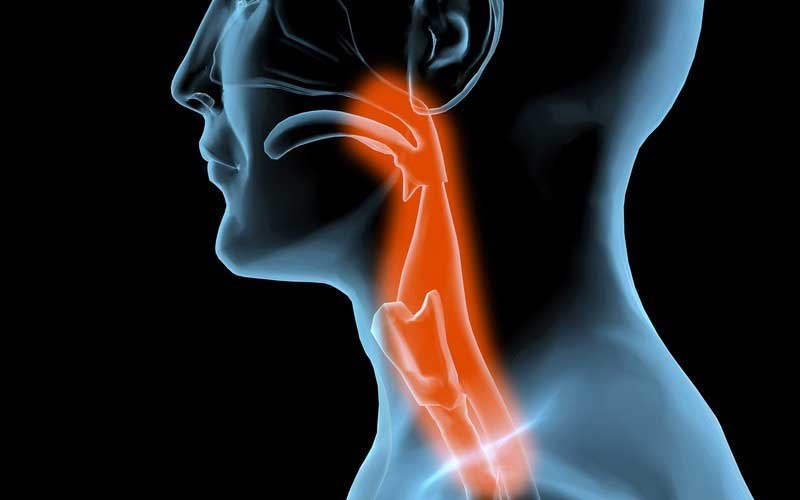
Swallowing impairment reduces quality of life complicates medication intake and leads to malnutrition and aspiration pneumonia which is a major cause of death in PD. More than 80 of patients with Parkinsons disease PD develop dysphagia during the course of their disease. Difficulty swallowing or dysphagia can happen at any stage of Parkinson disease and can be localized to the mouth throat and esophagus.
Dysphagia is a very frequent and highly relevant symptom in Parkinsons disease PD for quality of life morbidity and remaining lifetime which is unfortunately widely underdiagnosed and underestimated regarding patients centered care. Is Drooling secondary to a Swallowing Disorder in Patients with Parkinsons Disease Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2008.
Although most of these patients recover their swallowing function in a short period dysphagia in Parkinsons disease PD and Parkinson-related disorder PRD degenerates with disease progression.
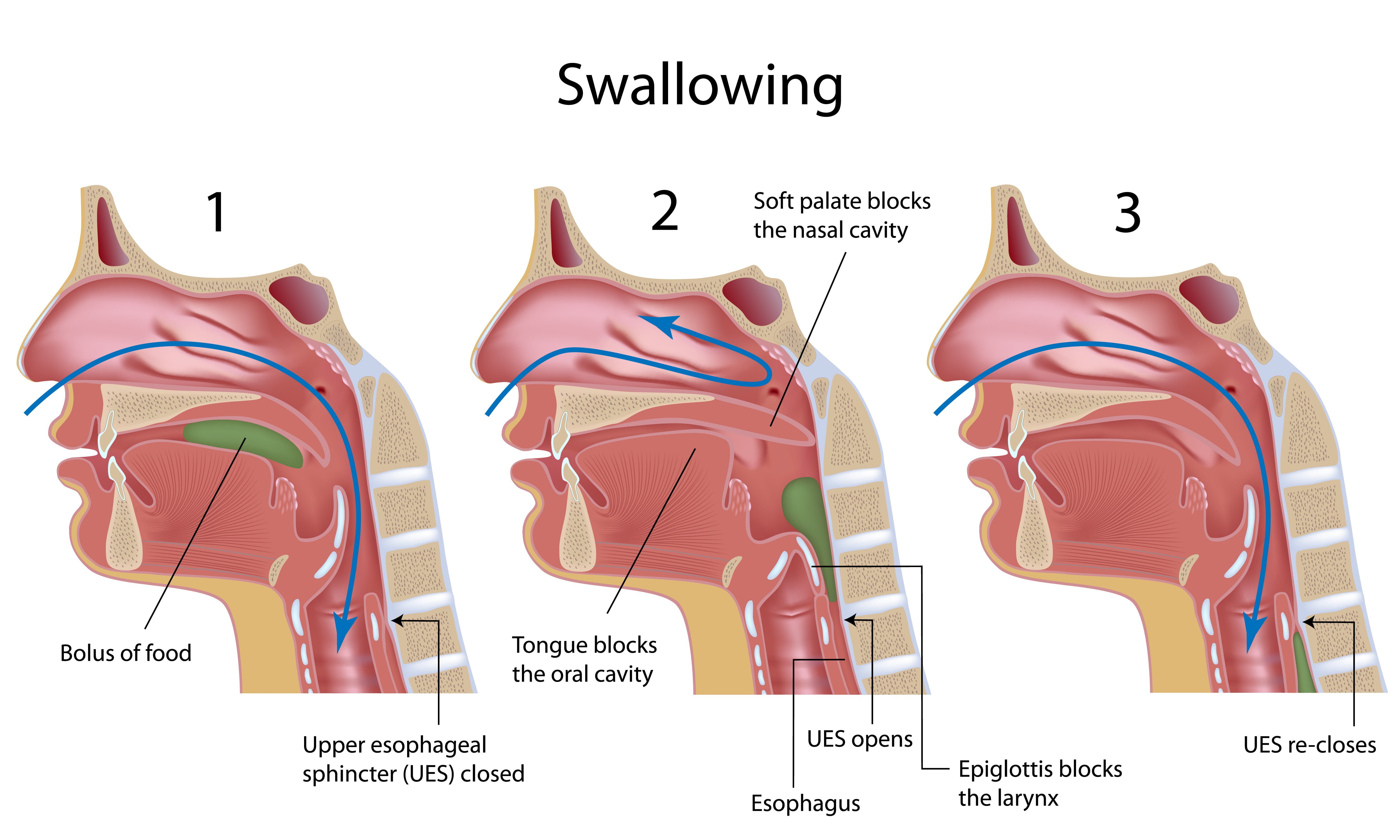
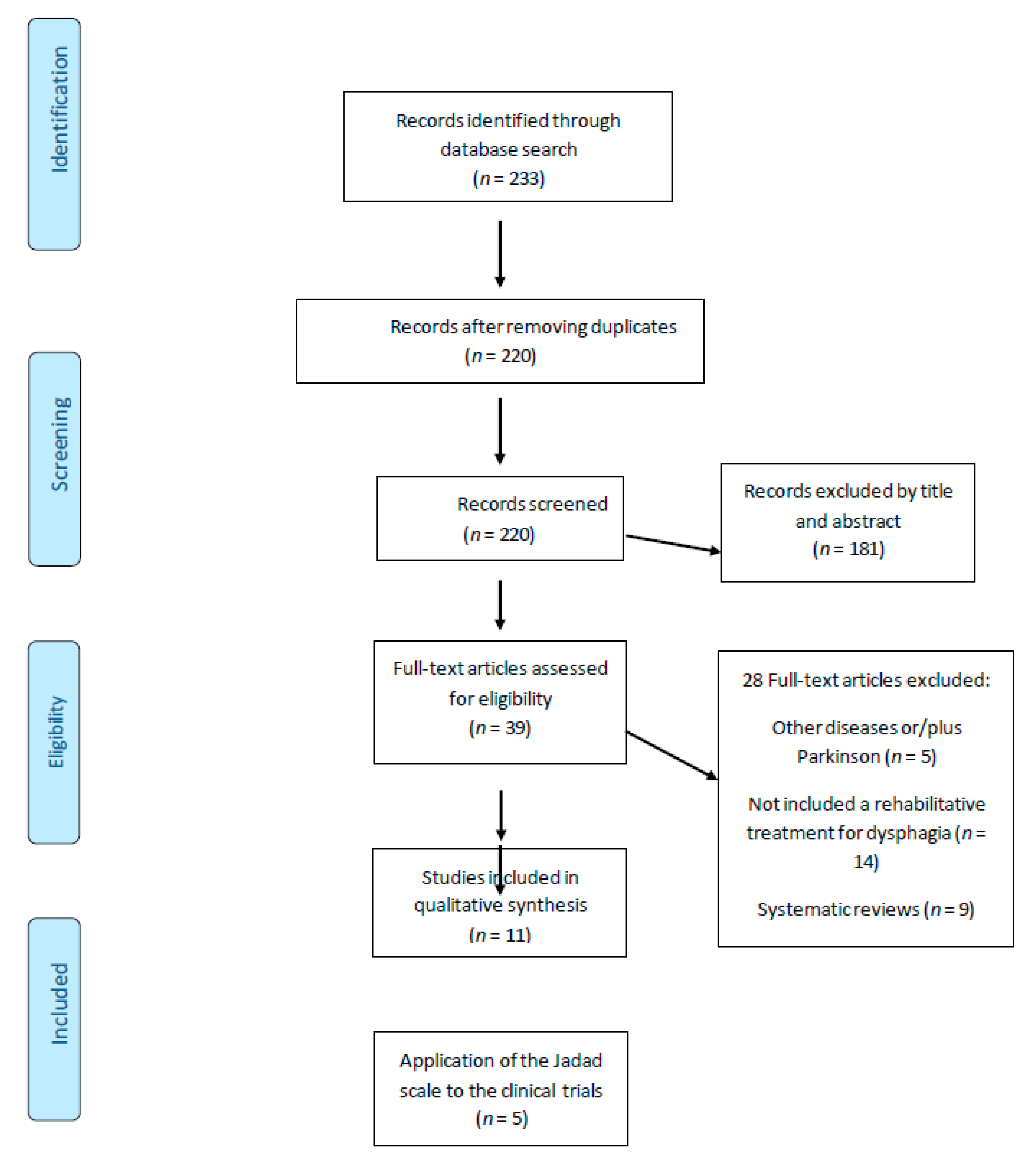
Is Drooling secondary to a Swallowing Disorder in Patients with Parkinsons Disease Parkinsonism Relat Disord 2008. The incidence of oropharyngeal dysphagia in Parkinsons disease PD is very high. Objective tests however indicate a higher frequency of dysphagia and this may be because patients may be asymptomatic and unaware of their swallowing difficulties until later in the disease course. Previous results should be interpreted cautiously as there is a lack of evidence to support the use of compensatory or rehabilitative approaches to dysphagia. 5 The swallowing difficulties most frequently associated with PD are related to the oral and pharyngeal phase resulting in abnormal bolus formation delayed swallowing reflex and prolongation of the pharyngeal transit time with repetitive swallows to. Dysphagia in Parkinsons Disease. Problems with tongue muscles. Although most of these patients recover their swallowing function in a short period dysphagia in Parkinsons disease PD and Parkinson-related disorder PRD degenerates with disease progression. Subtle signs of swallow dysfunction can include slow eating coughing with eating and weight loss.
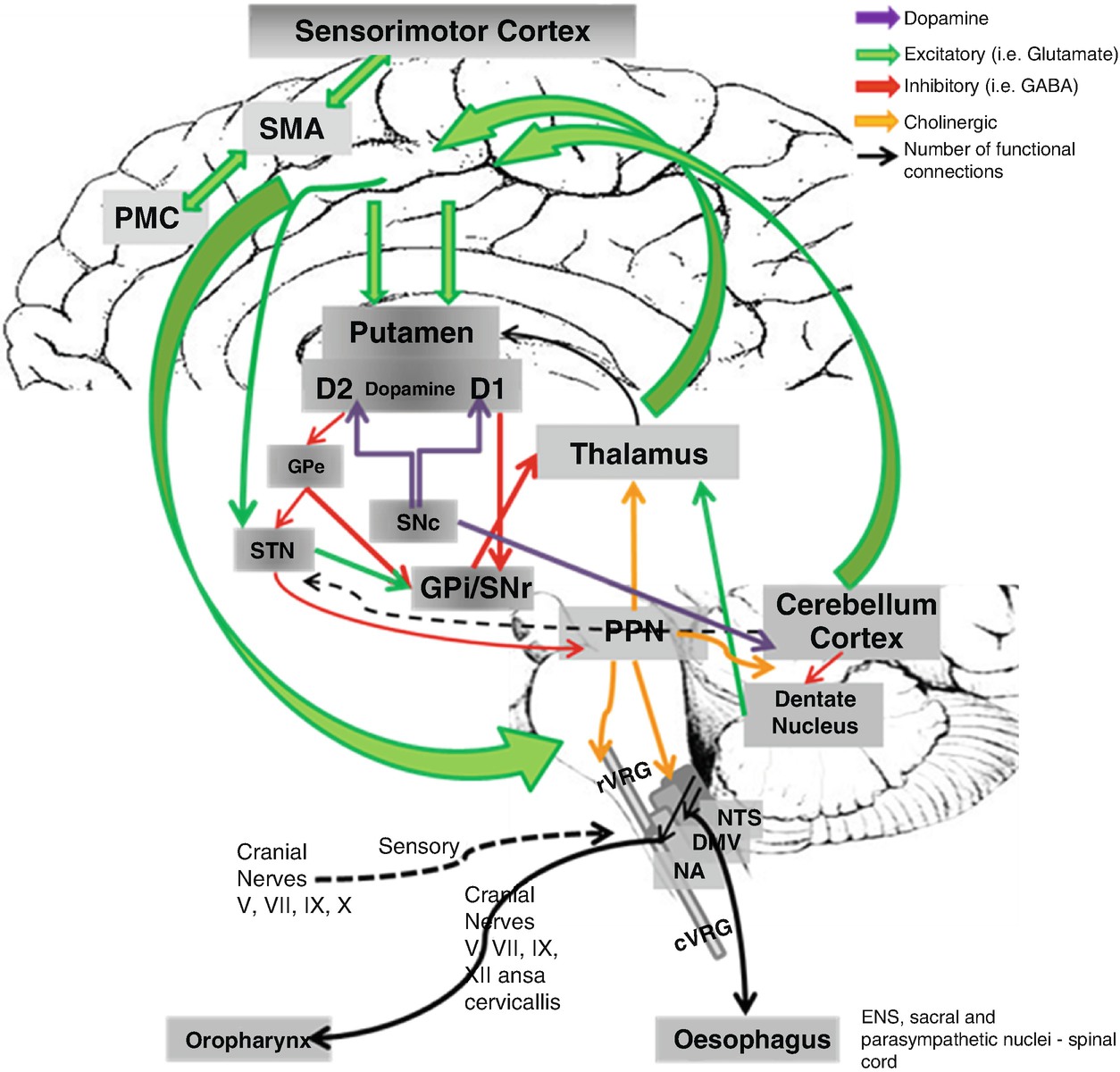
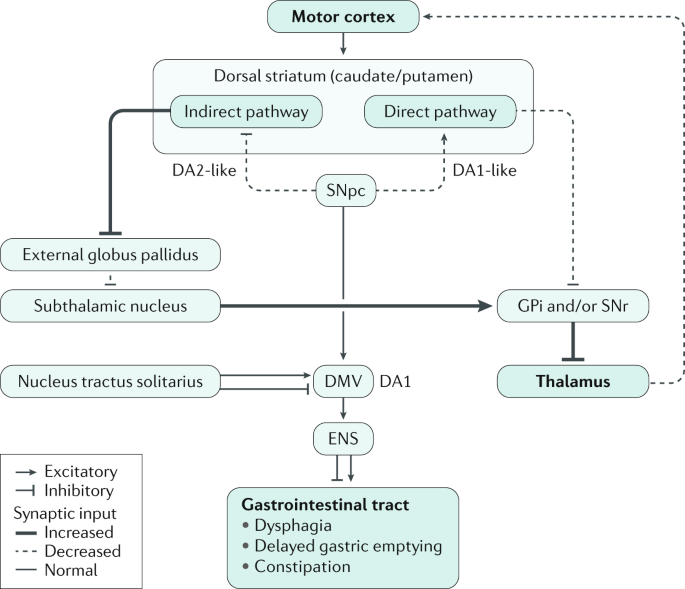
Dysfunction in Parkinsons Disease Dysphagia. Dysfunction in Parkinsons Disease Dysphagia. Although most of these patients recover their swallowing function in a short period dysphagia in Parkinsons disease PD and Parkinson-related disorder PRD degenerates with disease progression. Oropharyngeal and esophageal dysphagia are a frequent but seldom diagnosed symptom of Parkinsons disease PD. Dysphagia is very common in PD affecting over 80 of individuals reflecting the underlying motor impairments and the extent of the diseases progression. Muscle rigidity and bradykinesia are recognized as causes of swallowing dysfunction and it is diffi-cult to easily apply the strategies for stroke to the rehabilitation of dysphagia in PD patients. Parkinsons can cause the muscles in your jaw and face to be less efficient which affects the control you have over chewing and swallowing.














:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/swallowing-exercises-3146018-0bde224c9974460b8c691db922403943.jpg)














Post a Comment for "Parkinson's Disease And Dysphagia"